1. Dispatcher Servlet 개념
디스패처 서블릿에서 dispatch 는, 보내다라는 뜻을 가지고 있다. 이러한 단어를 포함하고 있는 디스패처 서블릿은 스프링 어플리케이션의 최전방에서 HTTP 프로토콜로 들어오는 모든 요청을 받아 적합한 컨트롤러에 위임하는 프론트 컨트롤러라 볼 수 있다.
보다 자세하게 설명을 하자면, 클라이언트로부터 어떤 요청이 오면 톰캣과 같은 서블릿 컨테이너가 요청을 받게 된다. 그리고 이 모든 요청을 프론트 컨트롤러인 디스패처 서블릿이 받아서 공통적인 작업을 수행한 뒤 해당 요청을 처리할 컨트롤러 빈을 getBean() 메소드로 호출해서 받아와 요청에 적합한 컨트롤러의 메소드를 실행시킨다. 예외가 발생했을 때 일관된 방식으로 처리하는 것 또한 프론트 컨트롤러인 디스패처 서블릿에서 담당하고 있다.
NOTE.
여기서 프론트 컨트롤러 (Front Controller) 라는 표현이 자주 사용되는데, 프론트 컨트롤러는 주로 서블릿 컨테이너의 제일 앞단에서 서버에 들어오는 클라이언트의 모든 요청을 받아 처리하는 컨트롤러로써, MVC 구조에서 함께 사용되는 디자인 패턴이다.
디스패처 서블릿의 장점
Spring MVC 는 디스패처 서블릿이 등장함에 따라 web.xml 의 역할을 상당히 축소시켰다. 기존에는 모든 서블릿에 대해서 URL 매핑을 하기 위해 web.xml 파일에 모두 등록해야 했지만, 디스패처 서블릿이 해당 어플리케이션으로 들어오는 모든 요청을 핸들링하고 공통 작업을 처리하면서 상당히 편리하게 이용이 가능해졌다.
디스패처 서블릿의 기능 처리를 표현하면 아래 그림과 같다.

디스패처 서블릿의 요청 처리 흐름
디스패처 서블릿이 모든 요청을 받아 각각의 컨트롤러로 매핑해주는 방식은 효율적으로 보인다. 하지만 디스패처 서블릿이 모든 요청을 처리하다보니 이미지나 HTML 등과 같은 정적 리소스에 대한 요청까지도 모두 가로채 정적 리소스를 불러오지 못하는 상황도 발생하곤 했다.
이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해 개발자들은 두 가지 방안을 고안했는데, 그 방안은 다음과 같다.
1. 정적 리소스에 대한 요청과 어플리케이션에 대한 요청 분리
첫 번째 방안은, 클라이언트의 요청 자체를 두 개로 분리하는 것이다.
- /apps 의 URL 로 접근할 경우 디스패처 서블릿이 처리를 담당
- /resources 의 URL 로 접근할 경우 디스패처 서블릿이 컨트롤할 수 없는 요청이므로 담당하지 않음
이러한 방식은, 앞서 언급한 문제는 해결할 수 있지만 소스 코드가 상당히 지저분해지며 모든 요청에 대해 /apps 나 /resources URL 을 붙여야 하므로 직관적인 설계가 될 수 없다.
2. 어플리케이션에 대한 요청을 탐색하고, 없을 경우 정적 리소스에 대한 요청으로 처리
두 번째 방안은 모든 요청에 대해 디스패처 서블릿이 적합한 컨트롤러를 탐색하고, 해당 요청에 대한 컨트롤러를 찾을 수 없는 경우에 2차적으로 설정된 정적 리소스 경로를 탐색해 리소스를 찾는 방식이다. 이렇게 영역을 분리하면 효율적인 리소스 관리가 가능할 뿐 아니라 추후에 확장이 용이하다는 장점을 가지게 된다.
2. ArrayList 객체를 복사하는 방법 2가지를 소개합니다.
- ArrayList 복사하기 - clone() - Shallow Copy
- ArrayList 복사하기 - Deep Copy
1. ArrayList 복사하기 - clone() - Shallow Copy
public Object clone()
보통 ArrayList를 복사할 때,
ArrayList의 clone() 메소드를 사용합니다.
이 메소드는 ArrayList 객체를 shallow copy한 복사본을 리턴합니다.
예제 1 - clone() 후, ArrayList의 데이터 변경
|
|
import java.util.ArrayList; |
|
|
|
|
|
public class CloneArrayList { |
|
|
public static void main(String[] args) { |
|
|
|
|
|
// 1. ArrayList 준비 |
|
|
ArrayList<Fruit> fruitList = new ArrayList<Fruit>(); |
|
|
fruitList.add(new Fruit("Apple", 1000)); |
|
|
fruitList.add(new Fruit("Banana", 2000)); |
|
|
|
|
|
// 2. ArrayList 복사 - clone() |
|
|
ArrayList<Fruit> copyOfFruitList = (ArrayList<Fruit>) fruitList.clone(); |
|
|
|
|
|
// 3. 복사된 결과 출력 |
|
|
System.out.println("=== ArrayList 복사(clone()) ==="); |
|
|
System.out.println("fruitList : " + fruitList); // [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
System.out.println("copyOfFruitList : " + copyOfFruitList); // [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
|
|
|
// 4. 원본 ArrayList 변경 |
|
|
fruitList.add(new Fruits("Orange", 500)); |
|
|
|
|
|
// 5. 결과 출력 |
|
|
System.out.println("=== 원본 ArrayList 변경 ==="); |
|
|
System.out.println("fruitList : " + fruitList); // [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ], [ Orange: 500 ]] |
|
|
System.out.println("copyOfFruitList : " + copyOfFruitList); // [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
} |
|
|
} |
|
|
|
|
|
class Fruit { |
|
|
|
|
|
private String name; |
|
|
private int price; |
|
|
|
|
|
public Fruit(String name, int price) { |
|
|
this.name = name; |
|
|
this.price = price; |
|
|
} |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
public String toString() { |
|
|
return "[ " + this.name + ": " + this.price + " ]"; |
|
|
} |
|
|
} |
예제 1 - 결과
|
|
=== ArrayList 복사(clone()) === |
|
|
fruitList : [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
copyOfFruitList : [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
|
|
|
=== 원본 ArrayList 변경 === |
|
|
fruitList : [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ], [ Orange: 500 ]] |
|
|
copyOfFruitList : [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
clone() 메소드를 사용하여 ArrayList를 복사하는 예제입니다.
0. Fruit Class 생성
먼저 Fruit 클래스를 작성하였습니다.
이 클래스는 name, price 속성을 가지고 있습니다.
1. 원본 ArrayList 생성
ArrayList<Fruit> fruitList = new ArrayList<Fruit>();
fruitList.add(new Fruit("Apple", 1000);
fruitList.add(new Fruit("Banana", 2000);
Fruit 객체를 element로 갖는 원본 ArrayList를 생성하고,
데이터를 추가하였습니다.
2. ArrayList 복사 - clone()
ArrayList<Fruit> copyOfFruitList = (ArrayList<Fruit>)fruitList.clone();
clone() 메소드를 사용하여, ArrayList 객체를 복사하였습니다.
3. 복사된 결과 출력
원본 ArrayList인 fruitList와
복사된 ArrayList인 copyOfFruitList를 출력하였습니다.
두, 객체의 값이 동일한 것을 확인 할 수 있습니다.
4. 원본 ArrayList 변경
fruitList.add(new Fruit("Orange", 500));
원본 ArrayList에 orange라는 Fruit 객체를 하나도 추가하였습니다.
5. 결과 출력
원본 ArrayList에만 새로운 Fruit 객체인 "orange"가 추가되고,
복사본에는 추가되지 않은 것을 확인 할 수 있습니다.
예제 2 - clone() 후, fruit 객체의 데이터 변경
그런데, ArrayList 원소의 추가, 삭제, 변경이 아닌,
ArrayList의 원소인 apple, banana 객체의 price값이 변경된다면 어떻게 될까요?
|
|
import java.util.ArrayList; |
|
|
|
|
|
public class CloneArrayList { |
|
|
public static void main(String[] args) { |
|
|
|
|
|
// 1. ArrayList 준비 |
|
|
ArrayList<Fruit> fruitList = new ArrayList<Fruit>(); |
|
|
fruitList.add(new Fruit("Apple", 1000)); |
|
|
fruitList.add(new Fruit("Banana", 2000)); |
|
|
|
|
|
// 2. ArrayList 복사 - clone() |
|
|
ArrayList<Fruit> copyOfFruitList = (ArrayList<Fruit>) fruitList.clone(); |
|
|
|
|
|
// 3. 복사된 결과 출력 |
|
|
System.out.println("=== ArrayList 복사(clone()) ==="); |
|
|
System.out.println("fruitList : " + fruitList); // [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
System.out.println("copyOfFruitList : " + copyOfFruitList); // [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
|
|
|
// 4. 원본 ArrayList의 apple의 price 변경 |
|
|
Fruit apple = fruitList.get(0); |
|
|
apple.setPrice(100); |
|
|
|
|
|
// 5. 결과 출력 |
|
|
System.out.println("=== 원본 ArrayList의 apple의 price 변경 ==="); |
|
|
System.out.println("fruitList : " + fruitList); // [[ Apple: 100 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
System.out.println("copyOfFruitList : " + copyOfFruitList); // [[ Apple: 100 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
} |
|
|
} |
|
|
|
|
|
class Fruit { |
|
|
|
|
|
private String name; |
|
|
private int price; |
|
|
|
|
|
public Fruit(String name, int price) { |
|
|
this.name = name; |
|
|
this.price = price; |
|
|
} |
|
|
|
|
|
public void setPrice(int price) { |
|
|
this.price = price; |
|
|
} |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
public String toString() { |
|
|
return "[ " + this.name + ": " + this.price + " ]"; |
|
|
} |
|
|
} |
예제 2 - 결과
|
|
=== ArrayList 복사(clone()) === |
|
|
fruitList : [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
copyOfFruitList : [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
|
|
|
=== 원본 ArrayList의 apple의 price 변경 === |
|
|
fruitList : [[ Apple: 100 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
copyOfFruitList : [[ Apple: 100 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
위 예제에서는 원본 ArrayList에 포함된 apple 객체의 가격을
아래와 같이 변경하였습니다.
Fruit apple = fruitList.get(0);
apple.setPrice(100);
fruitList(원본 ArrayList)의 0번째 원소인 fruit 객체의 가격을
1000원에서 100원으로 수정하였습니다.
변경후 결과를 보면,
원본 ArrayList(fruitList) 와 복사본 ArrayList(copyOfFruitList)의
apple 객체의 가격이 모두 변경된 것을 확인 할 수 있습니다.
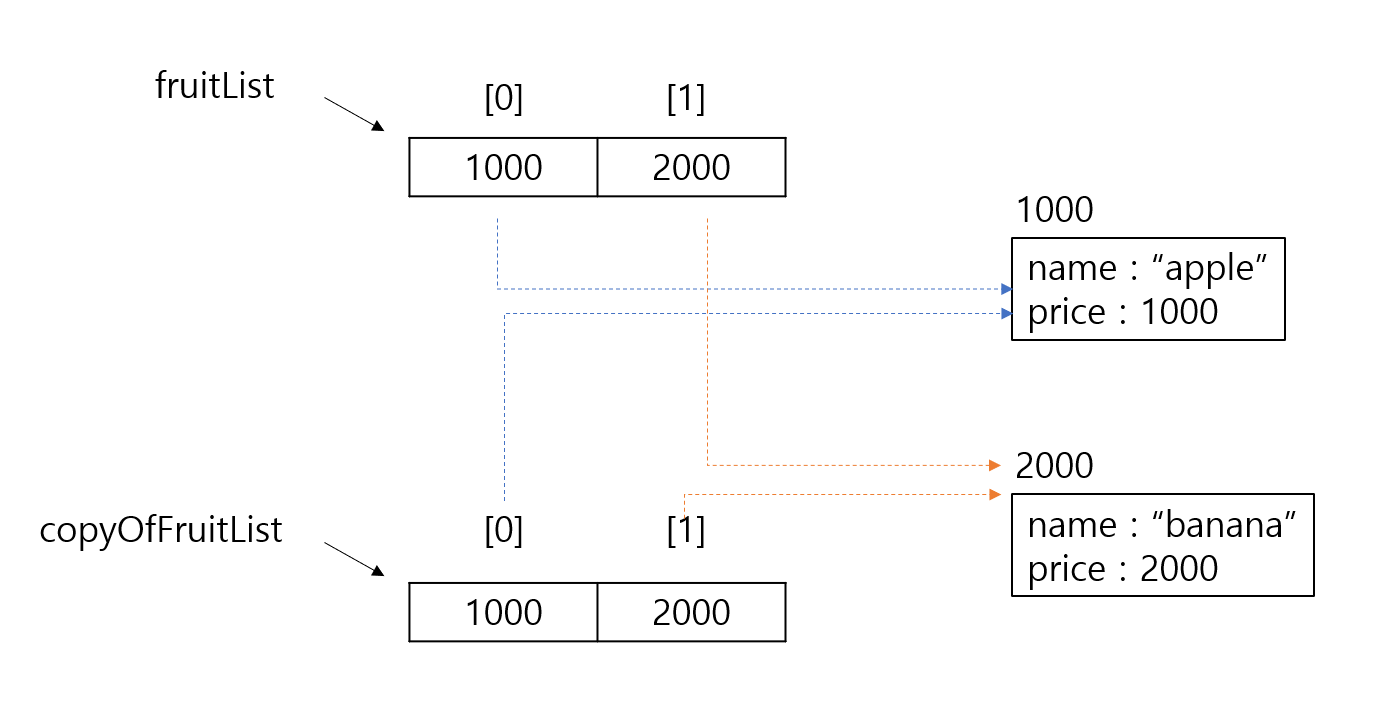
ArrayList에 객체를 넣으면,
ArrayList는 해당 객체를 가리키는 주소를 ArrayList에 저장합니다.
따라서, primitive 타입이 아닌, 객체를 clone()하면
ArrayList가 가진 객체의 주소를 복사하여,
복사된 ArrayList도 같은 객체를 가리키게 되는 것이죠.
따라서, 원본 ArrayList의 apple이라는 이름을 가지는 fruit 객체의 값을 수정하면,
복사본이 가리키는 객체는 동일하므로,
마치 복사본 ArrayList의 객체도 같이 변경된 것처럼 보이는 것입니다.
2. ArrayList 복사하기 - Deep Copy
ArrayList 안에 들어있는 element 객체까지 모두 복사해 주고 싶으면,
대상 객체에 cloneable 을 implement 하고,
clone() 메소드를 override하여,
ArrayList 안의 각각의 객체들을 clone() 해 주어야 합니다.
코드
|
|
import java.util.ArrayList; |
|
|
|
|
|
public class CloneArrayList { |
|
|
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { |
|
|
|
|
|
// 1. ArrayList 준비 |
|
|
ArrayList<Fruit> fruitList = new ArrayList<Fruit>(); |
|
|
fruitList.add(new Fruit("Apple", 1000)); |
|
|
fruitList.add(new Fruit("Banana", 2000)); |
|
|
|
|
|
// 2. ArrayList 복사 - 반복문과 객체의 clone() 이용 |
|
|
ArrayList<Fruit> copyOfFruitList = new ArrayList<Fruit>(); |
|
|
for (Fruit f : fruitList) { |
|
|
copyOfFruitList.add(f.clone()); |
|
|
} |
|
|
|
|
|
// 3. 복사된 결과 출력 |
|
|
System.out.println("=== ArrayList 복사(반복문과 객체의 clone() 이용) ==="); |
|
|
System.out.println("fruitList : " + fruitList); // [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
System.out.println("copyOfFruitList : " + copyOfFruitList); // [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
|
|
|
// 4. 원본 ArrayList의 apple의 price 변경 |
|
|
Fruit apple = fruitList.get(0); |
|
|
apple.setPrice(100); |
|
|
|
|
|
// 5. 결과 출력 |
|
|
System.out.println("=== 원본 ArrayList의 apple의 price 변경 ==="); |
|
|
System.out.println("fruitList : " + fruitList); // [[ Apple: 100 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
System.out.println("copyOfFruitList : " + copyOfFruitList); // [[ Apple: 100 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
} |
|
|
} |
|
|
|
|
|
class Fruit implements Cloneable { |
|
|
|
|
|
private String name; |
|
|
private int price; |
|
|
|
|
|
public Fruit(String name, int price) { |
|
|
this.name = name; |
|
|
this.price = price; |
|
|
} |
|
|
|
|
|
public void setPrice(int price) { |
|
|
this.price = price; |
|
|
} |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
public String toString() { |
|
|
return "[ " + this.name + ": " + this.price + " ]"; |
|
|
} |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
protected Fruit clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { |
|
|
return (Fruit) super.clone(); |
|
|
} |
|
|
} |
결과
|
|
=== ArrayList 복사(반복문과 객체의 clone() 이용) === |
|
|
fruitList : [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
copyOfFruitList : [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
|
|
|
=== 원본 ArrayList의 apple의 price 변경 === |
|
|
fruitList : [[ Apple: 100 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
|
|
copyOfFruitList : [[ Apple: 1000 ], [ Banana: 2000 ]] |
implements Cloneable, Override clone()
Fruit 클래스는 Cloneable 인터페이스를 implements하였습니다.
그리고, clone() 메소드를 Override 하였습니다.
이렇게하면, 객체의 clone() 메소드를 사용하여, 객체를 복사할 수 있습니다.
for(Fruit f : fruitList) {
copyOfFruitList.add(f.clone());
}
이렇게, ArrayList에 들어갈 클래스를 정의한 후,
반복문과 Fruit 클래스의 clone()를 이용하여,
element(Fruit객체)를 하나씩 새로운 배열에 복사해 줍니다.
이렇게 하면,
원본 배열 안의 fruit 객체의 price를 변경하더라도,
복사본의 fruit 객체는 변경되지 않습니다.
ArrayList의 원소를 복사하는 2가지 방법을 알아보았습니다.
'Study > 개발일지' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백엔드온라인TIL] java 학습 22일차 (0) | 2023.06.23 |
|---|---|
| [백엔드온라인TIL] java 학습 21일차 (0) | 2023.06.22 |
| [백엔드온라인TIL] java 학습 19일차 (0) | 2023.06.20 |
| [백엔드온라인TIL] java 학습 18일차 (0) | 2023.06.19 |
| [백엔드스터디WIL]4주차 학습일지 (1) | 2023.06.16 |


